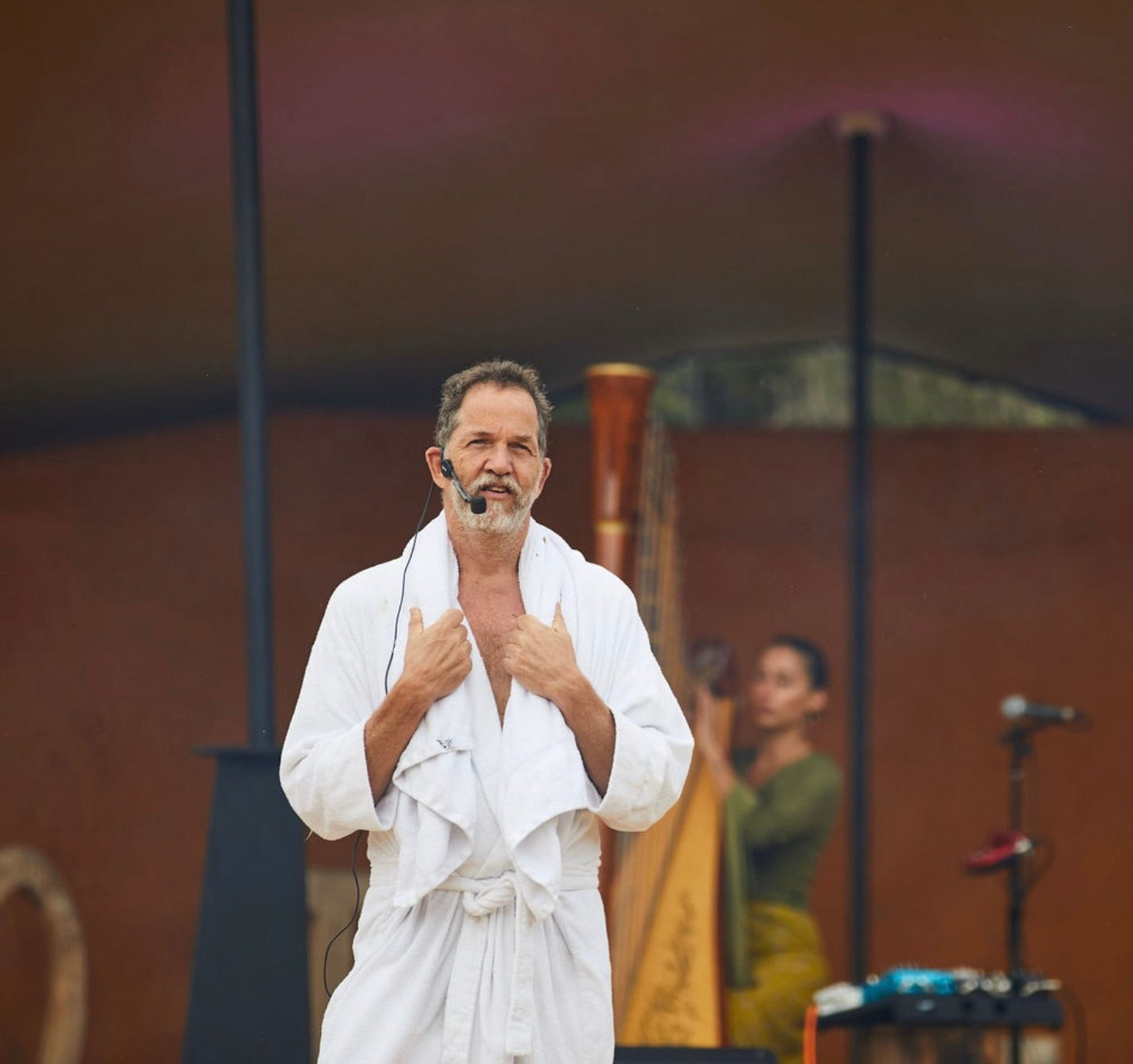
enter the saunabox
GIVEAWAY

Trusted by Athletes In:
The Science
Understanding the Physiological Effects of Heat Therapy
Mechanism: Heat exposure raises your body’s core temperature as you enter the sauna, leading to an increase in sweat production. Benefits: Helps in cooling the body through sweating and prepares it for enhanced detoxification and relaxation.

Mechanism: Exposure to heat increases body temperature, triggering the sweating mechanism. Sweating helps the body expel toxins and waste products through the skin. Benefits: Regular sweating through heat therapy can support detoxification by aiding in the removal of heavy metals, chemicals, and metabolic waste products.
Mechanism: Heat therapy induces vasodilation, which is the widening of blood vessels. This process improves blood flow and circulation, allowing more oxygen and nutrients to reach tissues. Benefits: Enhanced blood flow supports muscle relaxation, accelerates the healing process, and can help reduce pain and stiffness in conditions like arthritis and muscle strains.
Mechanism: Heat helps to relax muscles by increasing blood flow to the affected area, which reduces muscle tension and spasm. It also promotes the elasticity of muscle fibers and connective tissues. Benefits: This relaxation effect can alleviate muscle pain, stiffness, and soreness, making heat therapy a valuable tool for recovery and pain management.


Mechanism: Heat therapy raises the body’s core temperature, which in turn increases the metabolic rate. This heightened metabolic activity supports various physiological processes, including calorie expenditure Benefits: A higher metabolic rate supports metabolic health and can contribute to improved energy levels and overall metabolic function.
Mechanism: Heat stimulates the release of endorphins, providing a natural mood boost and stress relief. Benefits: Enhances mental well-being, reduces stress levels, and contributes to a sense of relaxation and calm.


Mechanism: The warm, humid air in saunas can help open airways, loosen mucus, and improve breathing. Benefits: Can be beneficial for individuals with respiratory conditions like asthma or bronchitis by aiding in easier breathing and reducing congestion.

Mechanism: After exiting the sauna, the body begins to cool down as it returns to its normal temperature. Rehydration helps to restore fluid balance lost through sweating. Benefits: Cooling down helps signal to your body that it’s time to wind down, which can promote better sleep. A lowered core temperature after a sauna session can align with your body’s natural sleep rhythm, leading to more restful sleep. Proper rehydration also supports overall recovery and maintains hydration levels essential for a good night’s rest.


Mechanism: Heat exposure raises your body’s core temperature as you enter the sauna, leading to an increase in sweat production. Benefits: Helps in cooling the body through sweating and prepares it for enhanced detoxification and relaxation.


Mechanism: Exposure to heat increases body temperature, triggering the sweating mechanism. Sweating helps the body expel toxins and waste products through the skin. Benefits: Regular sweating through heat therapy can support detoxification by aiding in the removal of heavy metals, chemicals, and metabolic waste products.


Mechanism: Heat therapy induces vasodilation, which is the widening of blood vessels. This process improves blood flow and circulation, allowing more oxygen and nutrients to reach tissues. Benefits: Enhanced blood flow supports muscle relaxation, accelerates the healing process, and can help reduce pain and stiffness in conditions like arthritis and muscle strains.


Mechanism: Heat helps to relax muscles by increasing blood flow to the affected area, which reduces muscle tension and spasm. It also promotes the elasticity of muscle fibers and connective tissues. Benefits: This relaxation effect can alleviate muscle pain, stiffness, and soreness, making heat therapy a valuable tool for recovery and pain management.


Mechanism: Heat therapy raises the body’s core temperature, which in turn increases the metabolic rate. This heightened metabolic activity supports various physiological processes, including calorie expenditure Benefits: A higher metabolic rate supports metabolic health and can contribute to improved energy levels and overall metabolic function.


Mechanism: Heat stimulates the release of endorphins, providing a natural mood boost and stress relief. Benefits: Enhances mental well-being, reduces stress levels, and contributes to a sense of relaxation and calm.


Mechanism: The warm, humid air in saunas can help open airways, loosen mucus, and improve breathing. Benefits: Can be beneficial for individuals with respiratory conditions like asthma or bronchitis by aiding in easier breathing and reducing congestion.


Mechanism: After exiting the sauna, the body begins to cool down as it returns to its normal temperature. Rehydration helps to restore fluid balance lost through sweating. Benefits: Cooling down helps signal to your body that it’s time to wind down, which can promote better sleep. A lowered core temperature after a sauna session can align with your body’s natural sleep rhythm, leading to more restful sleep. Proper rehydration also supports overall recovery and maintains hydration levels essential for a good night’s rest.






